Blackfire
Back to home
On this page
As the official Platform.sh observability service, Blackfire helps you improve the performance of your apps at each stage of their lifecycle. With Blackfire’s unique Application Performance Monitoring (APM) and Profiling features, you can achieve the following goals:
- Avoid performance bottlenecks by proactively identifying issues in your code
- Promptly solve identified issues by taking advantage of actionable recommendations
- Create performance budgets for critical parts of your app and get alerted of any problem before a change hits your production
Blackfire is installed natively on Platform.sh and works integrally with the Platform.sh workflow. This results in an effortless setup process and smooth user experience.
Note
Blackfire.io can be bundled with Enterprise and Elite subscriptions as part of the Observability Suite. To learn more, contact Sales. All customers can also subscribe to Blackfire separately.
Set up Blackfire 
On a Grid or Dedicated Gen 3 infrastructure 
If you’re using a plan with the Observability Suite, the Blackfire automated integration is enabled on your environments by default. Note that as an Observability Suite user, you can only access your Blackfire environments after you’ve been granted access to the related Platform.sh project. Therefore, to access your Blackfire environments, make sure you log in using your Platform.sh account.
If you have a Dedicated Gen 3 cluster or Grid environments without the Observability suite, you need to enable the integration yourself. To do so, follow these steps:
- Create a Blackfire account, preferably using your Platform.sh login.
- In your Blackfire account, create an organization. If you subscribed to Blackfire independently, your organization is automatically activated. If you subscribed to Blackfire through Platform.sh, ask Platform.sh Support to activate your organization.
- In your organization, create an environment.
- In your environment, click Settings/Environment Credentials.
- Retrieve your Blackfire server ID and server token.
- Follow the instructions from the Blackfire documentation.
If you’re using the Managed Fastly CDN, it’s already configured to operate with Blackfire. If you’re using a different Content Delivery Network (CDN), make sure you configure it to let Blackfire profile the code running on your servers.
On Dedicated Gen 2 infrastructure 
To install Blackfire on your Dedicated Gen 2 environments:
- Create a Blackfire account, preferably using your Platform.sh login.
- In your Blackfire account, create an organization. If you subscribed to Blackfire independently, your organization is automatically activated. If you subscribed to Blackfire through Platform.sh, ask Platform.sh Support to activate your organization.
- In your organization, create an environment.
- In your environment, click Settings/Environment Credentials.
- Retrieve your Blackfire server ID and server token.
- Send those credentials to Support so they complete the installation.
If you’re using the Managed Fastly CDN, it’s already configured to operate with Blackfire. If you’re using a different Content Delivery Network (CDN), make sure you configure it to let Blackfire profile the code running on your servers.
Automated integration 
Observability Suite
This feature is available as part of the Observability Suite. To add the Observability Suite to your project and take advantage of this feature, contact Sales.
The Blackfire automated integration is available for Grid and Dedicated Gen 3 environments.
When you create a new environment, it automatically triggers the creation of a Blackfire environment with the same settings. On this Blackfire environment, you have access to all the features provided by Blackfire. This includes monitoring, profiling, alerting, and build-related features.
When a Blackfire environment is created based on a Grid environment, user access settings are replicated from the Platform.sh Console to Blackfire.
This includes all access levels.
To access the Blackfire environment, each project user needs a Blackfire account. When a project user doesn’t already have a Blackfire account, a new one is automatically created using the user’s Platform.sh credentials.
You might have Blackfire variables already set on your project. In this case, the existing variables override the settings of the automated integration.
Note that to trigger the synchronization of changes to users and their access levels, you need to redeploy the environment.
Get started with Blackfire Monitoring 
Once Blackfire is set up on your infrastructure, to start monitoring your environment follow these steps:
1. Activate Blackfire Monitoring 
If you want to monitor a PHP or Python app, Blackfire Monitoring is available by default on your environments. You only need to specify which environments you want to monitor.
You can override the default behavior and deactivate Blackfire Monitoring by setting a env:BLACKFIRE_APM_ENABLED
environment variable with a value of 0.
To do so, create the following :
platform variable:create --level environment --prefix env: --name BLACKFIRE_APM_ENABLED --value 0 2. Enable Blackfire Monitoring on your environments 
To enable Blackfire Monitoring on your environments, follow these steps:
-
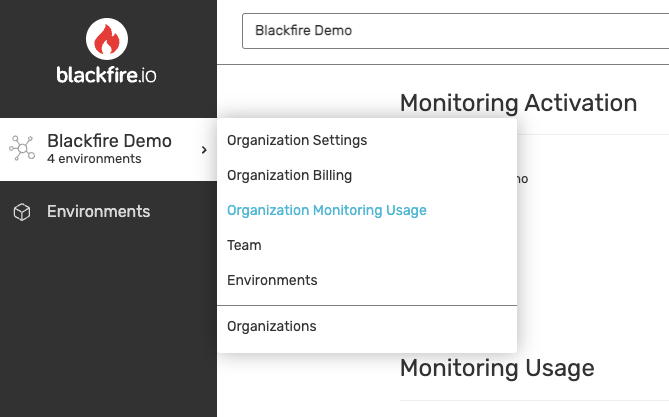
Go to your organizations list and select the organization where you want to enable Blackfire monitoring.
-
Click Organization Monitoring Usage.
-
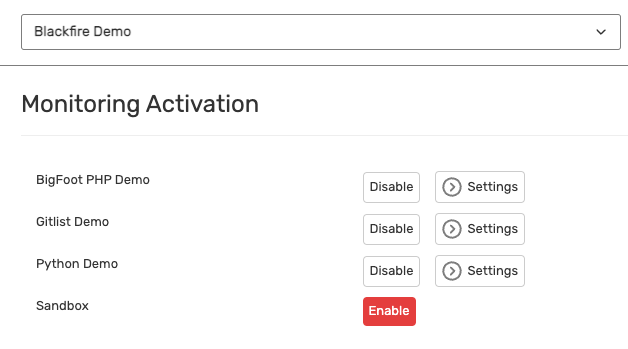
In the Monitoring Activation section, enable monitoring on the environments of your choice.
For more information on Blackfire monitoring features, see the Blackfire documentation.
Blackfire Profiling 
While your code is running, the Blackfire profiler collects deep performance metrics and provides full details and context of your code’s behavior. This helps you find the root cause of performance bottlenecks.
Blackfire lets you profile your application anywhere it’s deployed, including on your local development machines. Using a browser extension or CLI command, you can profile HTTP requests, CLI scripts, Consumers, and Daemons.
For more information on Blackfire profiling features, see the Blackfire documentation.
Test the performance of each new deployment 
Blackfire’s native integration with Platform.sh enables you to test your app’s performance every time you deploy a branch in production, staging, or development. Follow these steps:
-
Set up the Blackfire Builds integration.
-
Optional: set up an integration with your Git provider and get commit status updates from build reports.
-
To test business-critical use cases, write scenarios.
Troubleshooting 
Bypass your reverse proxy, load balancer or CDN 
To use Blackfire profiling, you need to bypass any reverse proxy, load balancer or CDN that sits in front of your app. See how to configure a bypass.
Configure your HTTP cache 
To take advantage of Blackfire features while using the HTTP cache with cookies,
allow the __blackfire cookie to go through the cache.
To do so, add a configuration similar to the following:
cache:
enabled: true
cookies: ["/SESS.*/", "__blackfire"] Get support 
If you’re experiencing issues with Blackfire and troubleshooting information doesn’t help, follow these steps:
- Retrieve startup errors.
- Retrieve your Blackfire logs.
- Send this data to Blackfire Support.
1. Retrieve startup errors 
To retrieve startup errors, run the following command:
platform ssh -- php -d display_startup_errors=on --ri blackfire 2. Retrieve your Blackfire logs 
To retrieve your Blackfire logs, follow these steps:
-
On the environment where you’re facing issues, create the following variable:
platform variable:create php:blackfire.log_file --value /tmp/blackfire.log -
To set the verbosity of the logs to level 4 (debug level), create the following variable:
platform variable:create php:blackfire.log_level --value 4 -
Start a profile or build.
-
To display the logs, run the following command:
platform ssh -- cat /tmp/blackfire.log > blackfire.log
After you’ve retrieved the logs, you can disable them. To do so, run the following commands:
platform variable:delete php:blackfire.log_file
platform variable:delete php:blackfire.log_level